算法思想
什么是算法?
在数学和计算机科学领域,算法是一系列有限的严谨指令,通常用于解决一类特定问题或执行计算
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation.
不正式的说,算法就是任何定义优良的计算过程:接收一些值作为输入,在有限的时间内,产生一些值作为输出。
Informally, an algorithm is any well-defined computational procedure that takes some value, or set of values, as input and produces some value, or set of values, as output in a finite amount of time.
贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm)
核心思想
- 将寻找最优解的问题分为若干个步骤
- 每一步骤都采用贪心原则,选取当前最优解
- 因为没有考虑所有可能,局部最优的堆叠不一定让最终解最优
贪心算法是一种在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优(即最有利)的选择,从而希望导致结果是最好或最优的算法。这种算法通常用于求解优化问题,如最小生成树、背包问题等。
常见问题及解答:
- 贪心算法一定会找到最优解吗? 答:不一定。贪心算法只保证在每一步选择中都是最优的,但并不能保证整个问题的最优解。例如,背包问题中的贪心算法可能会导致最后一个物品没有被装入背包。
- 如何判断一个问题是否适合用贪心算法解决? 答:一个问题如果可以用递归的方式分解成若干个子问题,且每个子问题都有明确的最优解(即局部最优),那么这个问题就可以用贪心算法解决。
- 贪心算法的时间复杂度是多少? 答:贪心算法的时间复杂度取决于问题的规模和具体实现。一般来说,对于规模较小的问题,贪心算法的时间复杂度可以达到O(nlogn)或O(n^2);对于规模较大的问题,可能需要O(n^3)或更高。
贪心算法的应用
- 选择排序,堆排序,拓扑排序,单源最短路径(Dijkstra),最小生成树(Prim、Kruskal),并查集的 union by size、union by height。
- 零钱兑换问题:给定一定数量的硬币和需要找零的金额,求使用最少的硬币数。
- Huffman 编码问题:给每一个符号分配编码,为出现频率高的符号分配较短的编码。
- 活动选择问题:在一个活动集合中,每次只能参加一个活动,问如何安排时间以最大化所有活动的收益。
- 背包问题:给定一组物品和一个背包,每个物品有一定的重量和价值,要求在不超过背包容量的情况下,尽可能多地装入物品。
Dijkstra
// ...
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
// 选取当前【距离最小】的顶点
Vertex curr = chooseMinDistVertex(list);
// 更新当前顶点邻居距离
updateNeighboursDist(curr);
// 移除当前顶点
list.remove(curr);
// 标记当前顶点已经处理过
curr.visited = true;
}- 没找到最短路径的例子:负边存在时,可能得不到正确解
- 问题出在贪心的原则会认为本次已经找到了该顶点的最短路径,下次不会再处理它(curr.visited = true)
- 与之对比,Bellman-Ford 并没有考虑局部距离最小的顶点,而是每次都处理所有边,所以不会出错,当然效率不如 Dijkstra
Prim
// ...
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
// 选取当前【距离最小】的顶点
Vertex curr = chooseMinDistVertex(list);
// 更新当前顶点邻居距离
updateNeighboursDist(curr);
// 移除当前顶点
list.remove(curr);
// 标记当前顶点已经处理过
curr.visited = true;
}Kruskal
// ...
while (list.size() < size - 1) {
// 选取当前【距离最短】的边
Edge poll = queue.poll();
// 判断两个集合是否相交
int i = set.find(poll.start);
int j = set.find(poll.end);
if (i != j) { // 未相交
list.add(poll);
set.union(i, j); // 相交
}
}零钱兑换问题
有几个解(零钱兑换 II)- 穷举法
public class Leetcode518 {
public int change(int[] coins, int amount) {
return rec(0, coins, amount, new LinkedList<>(), true);
}
/**
* 求凑成剩余金额的解的个数
*
* @param index 当前硬币索引
* @param coins 硬币面值数组
* @param remainder 剩余金额
* @param stack -
* @param first -
* @return 解的个数
*/
public int rec(int index, int[] coins, int remainder, LinkedList<Integer> stack, boolean first) {
if(!first) {
stack.push(coins[index]);
}
// 情况1:剩余金额 < 0 - 无解
int count = 0;
if (remainder < 0) {
print("无解:", stack);
}
// 情况2:剩余金额 == 0 - 有解
else if (remainder == 0) {
print("有解:", stack);
count = 1;
}
// 情况3:剩余金额 > 0 - 继续递归
else {
for (int i = index; i < coins.length; i++) {
count += rec(i, coins, remainder - coins[i], stack, false);
}
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.pop();
}
return count;
}
private static void print(String prompt, LinkedList<Integer> stack) {
ArrayList<Integer> print = new ArrayList<>();
ListIterator<Integer> iterator = stack.listIterator(stack.size());
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
print.add(iterator.previous());
}
System.out.println(prompt + print);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode518 leetcode = new Leetcode518();
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{1, 5, 10, 25}, 41);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{25, 10, 5, 1}, 41);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{5, 2, 1}, 5);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{1, 2, 5}, 5);
int count = leetcode.change(new int[]{15, 10, 1}, 21);
System.out.println(count);
}
}最优解(零钱兑换)
穷举法
public class Leetcode322 {
static int min = -1; // 需要的最少硬币数 2 3
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
rec(0, coins, amount, new AtomicInteger(-1), new LinkedList<>(), true);
return min;
}
// count 代表某一组合 钱币的总数
public void rec(int index, int[] coins, int remainder, AtomicInteger count, LinkedList<Integer> stack, boolean first) {
if (!first) {
stack.push(coins[index]);
}
count.incrementAndGet(); // count++
if (remainder == 0) {
System.out.println(stack);
if (min == -1) {
min = count.get();
} else {
min = Integer.min(min, count.get());
}
} else if (remainder > 0) {
for (int i = index; i < coins.length; i++) {
rec(i, coins, remainder - coins[i], count, stack, false);
}
}
count.decrementAndGet(); // count--
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode322 leetcode = new Leetcode322();
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{5, 2, 1}, 5);
int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{25, 10, 5, 1}, 41);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{2}, 3);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{15, 10, 1}, 21);
System.out.println(count);
}
}贪心法
public class Leetcode322 {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int remainder = amount;
int count = 0;
for (int coin : coins) {
while (remainder - coin > 0) {
remainder -= coin;
count++;
}
if (remainder - coin == 0) {
remainder = 0;
count++;
break;
}
}
if (remainder > 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return count;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode322 leetcode = new Leetcode322();
int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{5, 2, 1}, 5);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{25, 10, 5, 1}, 41);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{2}, 3);
// 问题1 没有回头,导致找到更差的解
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{15, 10, 1}, 21);
// 问题2 没有回头,导致无解
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{15, 10}, 20);
System.out.println(count);
}
}Huffman 编码问题
问题引入
什么是编码?
简单说就是建立【字符】到【数字】的对应关系,如下面大家熟知的 ASC II 编码表,例如,可以查表得知字符【a】对应的数字是十六进制数【0x61】
| \ | 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 0a | 0b | 0c | 0d | 0e | 0f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 0a | 0b | 0c | 0d | 0e | 0f |
| 0010 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | 1e | 1f |
| 0020 | 20 | ! | " | # | $ | % | & | ' | ( | ) | * | + | , | - | . | / |
| 0030 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | : | ; | < | = | > | ? |
| 0040 | @ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O |
| 0050 | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | [ | \ | ] | ^ | _ |
| 0060 | ` | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o |
| 0070 | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z | { | | | } | ~ | 7f |
注:一些直接以十六进制数字标识的是那些不可打印字符
传输时的编码
- java 中每个 char 对应的数字会占用固定长度 2 个字节
- 如果在传输中仍采用上述规则,传递 abbccccccc 这 10 个字符
- 实际的字节为 0061006200620063006300630063006300630063(16进制表示)
- 总共 20 个字节,不经济
现在希望找到一种最节省字节的传输方式,怎么办?
假设传输的字符中只包含 a,b,c 这 3 个字符,有同学重新设计一张二进制编码表,见下图
- 0 表示 a
- 1 表示 b
- 10 表示 c
现在还是传递 abbccccccc 这 10 个字符
- 实际的字节为 01110101010101010 (二进制表示)
- 总共需要 17 bits,也就是 2 个字节多一点,行不行?
不行,因为解码会出现问题,因为 10 会被错误的解码成 ba,而不是 c
- 解码后结果为 abbbababababababa,是错误的
怎么解决?必须保证编码后的二进制数字,要能区分它们的前缀(prefix-free)
用满二叉树结构编码,可以确保前缀不重复
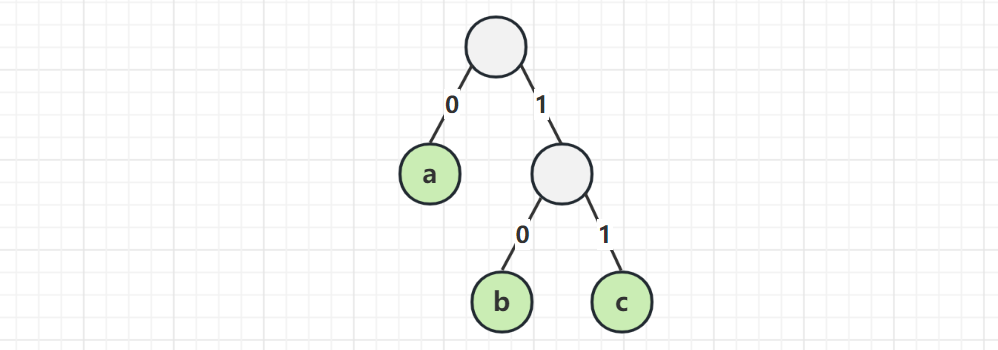
- 向左走 0,向右走 1
- 走到叶子字符,累计起来的 0 和 1 就是该字符的二进制编码
再来试一遍
- a 的编码 0
- b 的编码 10
- c 的编码 11
现在还是传递 abbccccccc 这 10 个字符
- 实际的字节为 0101011111111111111(二进制表示)
- 总共需要 19 bits,也是 2 个字节多一点,并且解码没有问题了,行不行?
这回解码没问题了,但并非最少字节,因为 c 的出现频率高(7 次)a 的出现频率低(1 次),因此出现频率高的字符编码成短数字更经济
考察下面的树
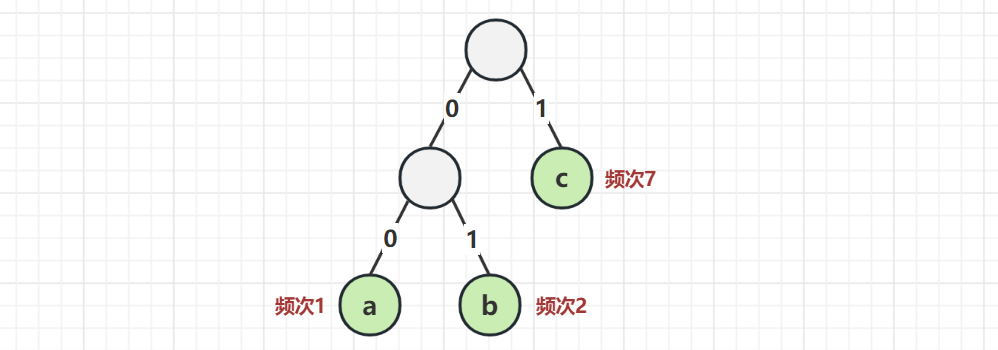
- 00 表示 a
- 01 表示 b
- 1 表示 c
现在还是传递 abbccccccc 这 10 个字符
- 实际的字节为 000101 1111111 (二进制表示)
- 总共需要 13 bits,这棵树就称之为 Huffman 树
- 根据 Huffman 树对字符和数字进行编解码,就是 Huffman 编解码
Huffman 树
public class HuffmanTree {
/*
Huffman 树的构建过程
1. 将统计了出现频率的字符,放入优先级队列
2. 每次出队两个频次最低的元素,给它俩找个爹
3. 把爹重新放入队列,重复 2~3
4. 当队列只剩一个元素时,Huffman 树构建完成
*/
static class Node {
Character ch; // 字符
int freq; // 频次
Node left;
Node right;
String code; // 编码
public Node(Character ch) {
this.ch = ch;
}
public Node(int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
int freq() {
return freq;
}
boolean isLeaf() {
return left == null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"ch=" + ch +
", freq=" + freq +
'}';
}
}
String str;
Map<Character, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public HuffmanTree(String str) {
this.str = str;
// 功能1:统计频率
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) {
/*if (!map.containsKey(c)) {
map.put(c, new Node(c));
}
Node node = map.get(c);
node.freq++;*/
Node node = map.computeIfAbsent(c, Node::new);
node.freq++;
}
// 功能2: 构造树
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(Node::freq));
queue.addAll(map.values());
while (queue.size() >= 2) {
Node x = queue.poll();
Node y = queue.poll();
int freq = x.freq + y.freq;
queue.offer(new Node(freq, x, y));
}
Node root = queue.poll();
// 功能3:计算每个字符的编码, 功能4:字符串编码后占用 bits
int sum = dfs(root, new StringBuilder());
for (Node node : map.values()) {
System.out.println(node + " " + node.code);
}
System.out.println("总共会占用 bits:" + sum);
}
private int dfs(Node node, StringBuilder code) {
int sum = 0;
if (node.isLeaf()) {
node.code = code.toString();
sum = node.freq * code.length();
} else {
sum += dfs(node.left, code.append("0"));
sum += dfs(node.right, code.append("1"));
}
if (code.length() > 0) {
code.deleteCharAt(code.length() - 1);
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HuffmanTree("abbccccccc");
}
}注意
- Node::new 是一个 Function,根据 key(即字符)生成 Node 对象
- 对应的是 public Node(Character ch) 有参构造
Huffman 编解码
补充两个方法,注意为了简单期间用了编解码都用字符串演示,实际应该按 bits 编解码
public class HuffmanTree {
// ...
// 编码
public String encode() {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : chars) {
sb.append(map.get(c).code);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// 解码
public String decode(String str) {
/*
从根节点,寻找数字对应的字符
数字是 0 向左走
数字是 1 向右走
如果没走到头,每走一步数字的索引 i++
走到头就可以找到解码字符,再将 node 重置为根节点
*/
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int i = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Node node = root;
while (i < chars.length) {
if (!node.isLeaf()) { // 非叶子
if(chars[i] == '0') { // 向左走
node = node.left;
} else if(chars[i] == '1') { // 向右走
node = node.right;
}
i++;
}
if (node.isLeaf()) {
sb.append(node.ch);
node = root;
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) {
HuffmanTree tree = new HuffmanTree("abbccccccc");
String encoded = tree.encode();
System.out.println(encoded);
System.out.println(tree.decode(encoded));
}
}注意
- 循环中非叶子节点 i 要自增,但叶子节点 i 暂不自增
- 第一个非叶子的 if 判断结束后,仍需要第二个叶子的 if 判断,因为在第一个 if 内 node 发生了变化
活动选择问题
public class ActivitySelectionProblem {
/*
要在一个会议室举办 n 个活动
- 每个活动有它们各自的起始和结束时间
- 找出在时间上互不冲突的活动组合,能够最充分利用会议室(举办的活动次数最多)
例1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
|-------)
|-------)
|-------)
例2
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
|---)
|---)
|-----------------------)
|-------)
|---)
|---------------)
几种贪心策略
1. 优先选择持续时间最短的活动
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
|---------------)
|-------)
|---------------)
2. 优先选择冲突最少的活动
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
|-------) 3
|-------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 2
|-----------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 4
|-------) 3
3. 优先选择最先开始的活动
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
|-----------------------------------)
|---)
|---)
|---)
4. 优先选择最后结束的活动
*/
static class Activity {
int index;
int start;
int finish;
public Activity(int index, int start, int finish) {
this.index = index;
this.start = start;
this.finish = finish;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Activity(" + index + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Activity[] activities = new Activity[]{
new Activity(0, 1, 3),
new Activity(1, 2, 4),
new Activity(2, 3, 5)
};
// Activity[] activities = new Activity[]{
// new Activity(0, 1, 2),
// new Activity(1, 3, 4),
// new Activity(2, 0, 6),
// new Activity(3, 5, 7),
// new Activity(4, 8, 9),
// new Activity(5, 5, 9)
// };
select(activities, activities.length);
}
public static void select(Activity[] activities, int n) {
List<Activity> result = new ArrayList<>();
int i, j;
i = 0;
result.add(activities[i]);
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (activities[j].start >= activities[i].finish) {
result.add(activities[j]);
i = j;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}分数背包问题
public class FractionalKnapsackProblem {
/*
1. n个物品都是液体,有重量和价值
2. 现在你要取走 10升 的液体
3. 每次可以不拿,全拿,或拿一部分,问最高价值是多少
编号 重量(升) 价值
0 4 24 水
1 8 160 牛奶 选中 7/8
2 2 4000 五粮液 选中
3 6 108 可乐
4 1 4000 茅台 选中
8140
简化起见,给出的数据都是【价值/重量】能够整除,避免计算结果中出现小数,增加心算难度
*/
static class Item {
int index;
int weight;
int value;
public Item(int index, int weight, int value) {
this.index = index;
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
}
int unitPrice() {
return value / weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Item(" + index + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item[] items = new Item[]{
new Item(0, 4, 24),
new Item(1, 8, 160),
new Item(2, 2, 4000),
new Item(3, 6, 108),
new Item(4, 1, 4000),
};
select(items, 10);
}
static void select(Item[] items, int total) {
Arrays.sort(items, Comparator.comparingInt(Item::unitPrice).reversed());
int remainder = total;
int max = 0;
for (Item item : items) {
if (remainder - item.weight > 0) {
max += item.value;
remainder -= item.weight;
} else {
max += remainder * item.unitPrice();
break;
}
}
System.out.println("最高价值为:" + max);
}
}0-1 背包问题
可能得不到最优解
public class KnapsackProblem {
/*
1. n个物品都是固体,有重量和价值
2. 现在你要取走不超过 10克 的物品
3. 每次可以不拿或全拿,问最高价值是多少
编号 重量(g) 价值(元)
0 1 1_000_000 钻戒一枚
1 4 1600 黄金一块
2 8 2400 红宝石戒指一枚
3 5 30 白银一块
*/
static class Item {
int index;
int weight;
int value;
public Item(int index, int weight, int value) {
this.index = index;
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
}
public int unitValue() {
return value / weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Item(" + index + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item[] items = new Item[]{
new Item(0, 1, 1_000_000),
new Item(1, 4, 1600),
new Item(2, 8, 2400),
new Item(3, 5, 30)
};
select(items, 10);
}
static void select(Item[] items, int total) {
Arrays.sort(items, Comparator.comparingInt(Item::unitValue).reversed());
int max = 0; // 最大价值
for (Item item : items) {
System.out.println(item);
if (total >= item.weight) { // 可以拿完
total -= item.weight;
max += item.value;
} else { // 拿不完
// max += total * item.unitValue();
// break;
}
}
System.out.println("最大价值是:" + max);
}
}贪心算法的局限
| 问题名称 | 是否能用贪心得到最优解 | 替换解法 |
|---|---|---|
| Dijkstra(不存在负边) | ✔️ | |
| Dijkstra(存在负边) | ❌ | Bellman-Ford |
| Prim | ✔️ | |
| Kruskal | ✔️ | |
| 零钱兑换 | ❌ | 动态规划 |
| Huffman 树 | ✔️ | |
| 活动选择问题 | ✔️ | |
| 分数背包问题 | ✔️ | |
| 0-1 背包问题 | ❌ | 动态规划 |
动态规划(Dynamic-Programming)
核心思想
- Programming - 在这里指用数学方法来根据子问题求解当前问题(通俗理解就是找到递推公式)
- Dynamic - 指缓存子问题结果,根据子问题结果计算当前结果(多阶段进行,可以进一步优化)
动态规划的应用
- 斐波那契数列: 计算第n项斐波那契数。
- 背包问题: 在给定的背包容量下,选择物品以使总价值最大。
- 最长公共子序列: 在两个序列中,找到最长的公共子序列。
Fibonacci
普通版
用一维数组缓存子问题结果
public class Fibonacci {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fibonacci(13));
}
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
if (n < 2) {
return dp[n];
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 2] + dp[i - 1];
}
return dp[n];
}
}降维
前面讲过,缓存子问题结果是可以优化的,比如二维变一维,一维变零维(零维指用变量缓存子问题结果)
public class Fibonacci {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fibonacci(13));
}
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int c = b + a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
}最短路径 - Bellman-Ford
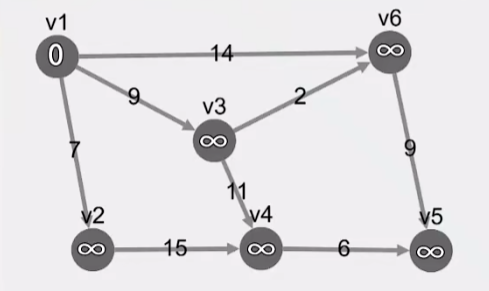
如图,求从起点 v1 到 v4 的最短路径
我们可以将问题做如下分解:
先分别求 v1 到 v3 和 v2 的最短距离,在这两个的基础上,我们再看,从 v1 出发是经过 v2 还是 v3 到达 v4 的距离更短
public class BellmanFord {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
/*
f(v) 用来表示从起点出发,到达 v 这个顶点的最短距离
初始时
f(v) = 0 当 v==起点 时
f(v) = ∞ 当 v!=起点 时
之后
新 旧 所有from
f(to) = min(f(to), f(from) + from.weight)
from 从哪来
to 到哪去
f(v4) = min( ∞, f(v3) + 11 ) = 20
f(v4) = min( 20, f(v2) + 15 ) = 20
v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6
0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞
0 7 9 ∞ ∞ 14 第一轮
0 7 9 20 23 11 第二轮
0 7 9 20 20 11 第三轮
0 7 9 20 20 11 第四轮
0 7 9 20 20 11 第五轮
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Edge> edges = List.of(
new Edge(6, 5, 9),
new Edge(4, 5, 6),
new Edge(1, 6, 14),
new Edge(3, 6, 2),
new Edge(3, 4, 11),
new Edge(2, 4, 15),
new Edge(1, 3, 9),
new Edge(1, 2, 7)
);
int[] dp = new int[7]; // 一维数组用来缓存结果
dp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < dp.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
print(dp);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (Edge e : edges) {
if(dp[e.from] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
dp[e.to] = Integer.min(dp[e.to], dp[e.from] + e.weight);
}
}
}
print(dp);
}
static void print(int[] dp) {
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(dp)
.mapToObj(i -> i == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "∞" : String.valueOf(i))
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", "]")));
}
}其实在我之前的笔记中,贝尔曼-福德算法的另一个实现也体现了动态规划的思想,只是那个将子问题的结果保存在顶点类的一个属性里[数据结构 | Javaer小智的编程笔记]
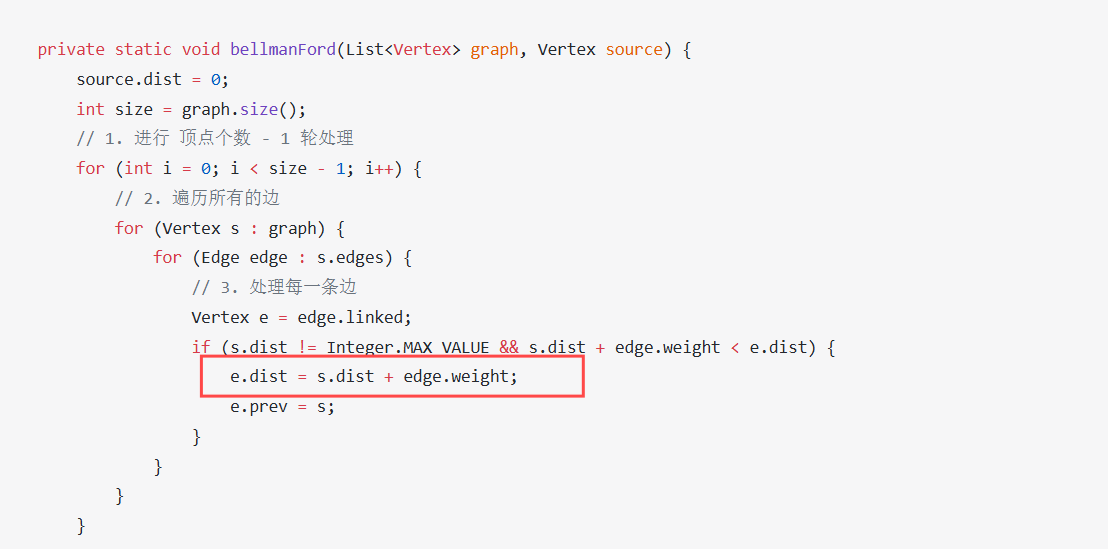
不同路径
机器人要从左上角走到右下角,每次只能向右或向下,问一共有多少条不同路径?
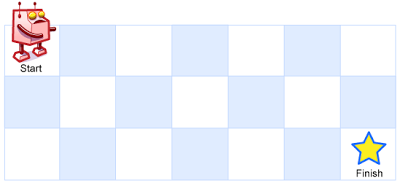
分析,先考虑较为简单的情况
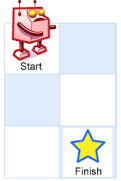
可能路径有三种情况:
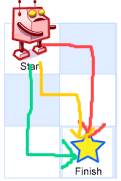
- 👉 👇 👇
- 👇 👇👉
- 👇👉👇
分析:设坐标为,共有 m 行 n 列
(0,0) (0,1)
(1,0) (1,1)
(2,0) (2,1)如果终点是 (0,1) 那么只有一种走法
如果终点是 (1,0) 那么也只有一种走法
如果终点是 (1,1) 呢,它的走法是从它的上方走下来,或者从它的左边走过来,因此走法 = f(0,1) + f(1,0) = 2种
如果终点是 (2,0) 那么也只有一种走法
如果终点是 (2,1) 呢,它的走法是从它的上方走下来,或者从它的左边走过来,因此走法 = f(1,1) + f(2,0) = 3种
总结规律发现:
- 终点是 (0,1) (0,2) (0,3) ... (0,n) 走法只有1种
- 终点是 (1,0) (2,0) (3,0) ... (m,0) 走法也只有1种
- 除了上面两种情况以外,(i,j) 处的走法等于(i-1,j) + (i,j-1) 的走法之和,即为递推公式
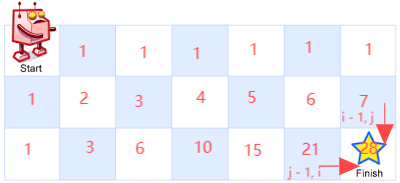
题解
public class UniquePaths {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = new UniquePaths().uniquePaths(3, 7);
System.out.println(count);
}
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}降维
由于每次更新只依赖于当前行和前一行的值,因此可以将二维数组降维为一维数组,从而节省空间
public class UniquePaths {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = new UniquePaths().uniquePaths(3, 7);
System.out.println(count);
}
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
dp[0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
}0-1 背包
- n类物品都是固体,有重量和价值,且只有一个
- 在你要取走不超过 10 克的物品
- 每次可以不拿或全拿,问最高价值是多少
| 编号 | 重量(g) | 价值(元) | 物品 | 简称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 1600 | 黄金 | A |
| 1 | 8 | 2400 | 红宝石 | R |
| 2 | 5 | 30 | 白银 | S |
| 3 | 1 | 1_000_000 | 钻石 | D |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0 0 0 0 0 A A A A A A A 黄金
1 0 0 0 0 A A A A R R R 红宝石
2 0 0 0 0 A A A A R R R 白银
3 0 D D D D DA DA DA DA DR DR 钻石
行代表物品编号 i,列代表要取走物品不超过的重量 j
表中每一个位置 (i, j) 表示在0 ~ i 号物品中取走不超过 j 克的物品的最优解
意味着最右下角最后一个位置表示在 0 ~ 4 号物品中取走不超过 10 克的物品的最优解,也就是我们最终想要的答案
每一个位置是一个区域问题,如何确定每个位置对应的最优解是什么?
其实就两种情况,不取走编号为 i 的物品和要取走编号为 i 的物品
如果编号为 i 的物品的重量超过 j,那就不取,反之则取
如果不取,那么 (i, j) 处的最优解就是前一行 j 处的最优解,也就是 (i - 1, j) 处
如果取,那么我们要考虑 i 物品的价值,当然 i 物品取完,背包可能还会剩下空间,我们还需要加上剩下空间能取走除 i 之外的物品的最优解,也就是 (i - 1, j - i.weight) 处的最优解
然后让 i.value 与 (i - 1, j - i.weight) 处的最优解相加,与前一行 j 处 (i - 1, j) 的最优解做比较,大的即为 (i, j) 处的最优解
整个过程的核心伪代码如下:
if(不取) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
} else { 取
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], item.value + dp[i-1][j-item.weight])
}public class KnapsackProblem {
static class Item {
int index;
String name;
int weight;
int value;
public Item(int index, String name, int weight, int value) {
this.index = index;
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Item(" + name + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item[] items = new Item[]{
new Item(1, "黄金", 4, 1600),
new Item(2, "宝石", 8, 2400),
new Item(3, "白银", 5, 30),
new Item(4, "钻石", 1, 10_000),
};
System.out.println(select(items, 10));
}
static int select(Item[] items, int total) {
int[][] dp = new int[items.length][total + 1];
print(dp);
Item item0 = items[0];
for (int j = 0; j < total + 1; j++) {
if (j >= item0.weight) {
dp[0][j] = item0.value;
}
}
print(dp);
for (int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) {
Item item = items[i];
for (int j = 1; j < total + 1; j++) {
// x: 上一次同容量背包的最大价值
int x = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= item.weight) {
// j-item.weight: 当前背包容量-这次物品重量=剩余背包空间
// y: 剩余背包空间能装下的最大价值 + 这次物品价值
int y = dp[i - 1][j - item.weight] + item.value;
dp[i][j] = Integer.max(x, y);
} else {
dp[i][j] = x;
}
}
print(dp);
}
return dp[dp.length - 1][total];
}
static void print(int[][] dp) {
System.out.println(" " + "-".repeat(63));
Object[] array = IntStream.range(0, dp[0].length + 1).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%5d ".repeat(dp[0].length)) + "%n", array);
for (int[] d : dp) {
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%5d ".repeat(d.length)) + "%n", array);
}
}
}降维
static int select(Item[] items, int total) {
int[] dp = new int[total + 1];
for (Item item : items) {
for (int j = total; j > 0; j--) {
if (j >= item.weight) { // 装得下
dp[j] = Integer.max(dp[j], item.value + dp[j - item.weight]);
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return dp[total];
}注意:内层循环需要倒序,否则 dp[j - item.weight] 的结果会被提前覆盖
完全背包
- n类物品都是固体,有重量和价值,且都有无限多个
- 在你要取走不超过 10 克的物品
- 每次可以不拿或全拿,问最高价值是多少
完全背包问题和 0-1 背包问题很像,主要区别在与同类物品可以取走的数量
完全背包问题的核心伪代码如下
if(不取) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
} else { 取
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], item.value + dp[i][j-item.weight])
}可以看出,完全背包问题和 0-1 背包问题在解决思路上的区别主要在于当取走 i 物品时,减去 i 物品重量后背包剩下空间是否可以再取一次 i 物品,如果取,剩下空间能取走物品的最优解对应在 (i, j - item.weight) 处,反之则在(i - 1, j - item.weight) 处。
public class KnapsackProblemComplete {
static class Item {
int index;
String name;
int weight;
int value;
public Item(int index, String name, int weight, int value) {
this.index = index;
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Item(" + name + ")";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item[] items = new Item[]{
new Item(1, "青铜", 2, 3), // c
new Item(2, "白银", 3, 4), // s
new Item(3, "黄金", 4, 7), // a
};
System.out.println(select(items, 6));
}
/*
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 0 0 c c cc cc ccc
2 0 0 c s cc cs ccc
3 0 0 c s a a ac
*/
private static int select(Item[] items, int total) {
int[][] dp = new int[items.length][total + 1];
Item item0 = items[0];
for (int j = 0; j < total + 1; j++) {
if (j >= item0.weight) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - item0.weight] + item0.value;
}
}
print(dp);
for (int i = 1; i < items.length; i++) {
Item item = items[i];
for (int j = 1; j < total + 1; j++) {
// x: 上一次同容量背包的最大价值
int x = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= item.weight) {
// j-item.weight: 当前背包容量-这次物品重量=剩余背包空间
// y: 剩余背包空间能装下的最大价值 + 这次物品价值
int y = dp[i][j - item.weight] + item.value;
dp[i][j] = Integer.max(x, y);
} else {
dp[i][j] = x;
}
}
print(dp);
}
return dp[dp.length - 1][total];
}
static void print(int[][] dp) {
System.out.println(" " + "-".repeat(63));
Object[] array = IntStream.range(0, dp[0].length + 1).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%5d ".repeat(dp[0].length)) + "%n", array);
for (int[] d : dp) {
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%5d ".repeat(d.length)) + "%n", array);
}
}
}降维
private static int select(Item[] items, int total) {
int[] dp = new int[total + 1];
for (Item item : items) {
for (int j = 0; j < total + 1; j++) {
if (j >= item.weight) {
dp[j] = Integer.max(dp[j], dp[j - item.weight] + item.value);
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return dp[total];
}注意:与 0-1 背包问题相反,内层循环不能倒序,因为这里需要被覆盖后的 dp[j - item.weight] 的结果
零钱兑换
在算法设计中,零钱兑换问题是一个经典的动态规划问题。其核心在于:给定不同面额的硬币和一个总金额,计算出组成该金额的最少硬币数量。如果无法组成该金额,则返回 -1。
零钱兑换问题与完全背包问题的相似性
零钱兑换问题与完全背包问题在整体实现上有诸多相似之处:
- 总金额:相当于背包的容量。
- 硬币面值:对应物品的重量。
- 硬币个数:视为物品的价值(固定为1,且求最小)。
然而,两者也存在关键差异:
- 目标:完全背包问题旨在最大化背包的总价值,而零钱兑换问题则是最小化所需硬币的数量。
- 约束条件:完全背包问题关注“总价值不超过背包容量”,而零钱兑换问题要求“恰好凑满总金额”。
下表每个位置表示凑满金额的硬币组合的最优解
比如,在 (2, 3) 这个位置,表示的就是在面值为1、2 中,凑满金额 3 的硬币组合的最优解为 一个面值为 1 和一个面值为 2 的硬币
面值 0 1 2 3 4 5
1 0 1 11 111 1111 11111
2 0 1 2 21 22 221
5 0 1 2 21 22 5
面值 0 1 2 3 4 5
10 0 max max max max max核心伪代码如下
if(不取) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
} else { 取
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j], 1 + dp[i][j - coins[i]])
}且要注意在初始化第一行的数据时,如果金额无法凑满,应初始化为 max = amount + 1
public class ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode322 {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length][amount + 1];
for (int j = 1; j < amount + 1; j++) {
if (j >= coins[0]) {
dp[0][j] = 1 + dp[0][j - coins[0]];
} else {
dp[0][j] = max;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < coins.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < amount + 1; j++) {
if (j >= coins[i]) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], 1 + dp[i][j - coins[i]]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
print(dp);
}
int r = dp[coins.length - 1][amount];
return r > amount ? -1 : r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode322 leetcode = new ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode322();
int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{1, 2, 5}, 5);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{25, 10, 5, 1}, 41);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{2}, 3);
// int count = leetcode.coinChange(new int[]{15, 10, 1}, 21);
System.out.println(count);
}
static void print(int[][] dp) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(18));
Object[] array = IntStream.range(0, dp[0].length + 1).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%2d ".repeat(dp[0].length)) + "%n", array);
for (int[] d : dp) {
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%2d ".repeat(d.length)) + "%n", array);
}
}
}关于 dp[0][j] = max 的解释
在动态规划的二维数组中,dp[0][j] 表示使用前 0 种硬币凑成金额 j 所需的最少硬币数。由于没有硬币可用,无法凑成任何金额,因此我们将其初始化为一个较大的值(max),表示无法凑成该金额。这样,在后续的状态转移中,如果某个状态的值仍为 max,则说明该金额无法通过当前的硬币组合凑成。
max表示的是一个状态,而不是一个固定的数,当然max最小应为amount + 1,才可以表示金币无法凑满的状态,原因如下:
当要凑满金额 amount 时,我们需要的硬币数量最多就是 amount,因为 coins 中的可能存在的硬币面值最小为 1 ,比如当要凑满金额 5 时,我们需要的硬币数量最多就是 5,因此只要max > amount,我们就可以拿他来表示无法凑满金额的状态
我们一开始将max定义为amount + 1,随着后续的状态转移,max可能会变成amount + 2、+3、...、+n,但始终大于要凑满的金额 amount,所以最后返回结果时,我们可以以此来判断凑满金额amount是否有解
降维
一开始除 0 外的其他位置全初始化为 amount + 1 表示,在 coins 里没有硬币时要凑满总金额 1 ~ amount 都是无解
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1);
//总金额为 0,最优解恒为 0
dp[0] = 0;
for (int coin : coins) {
for (int j = coin; j < amount + 1; j++) {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], 1 + dp[j - coin]);
}
}
int r = dp[amount];
return r > amount ? -1 : r;
}零钱兑换 II
public class ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode518 {
/*
面值 0 1 2 3 4 5 总金额-背包容量
1 1 1 11 111 1111 11111
2 1 1 11 111 1111 11111
2 21 211 2111
22 221
5 1 1 11 111 1111 11111
2 21 211 2111
22 221
5
if(放得下)
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-coin]
else(放不下)
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
*/
public int change(int[] coins, int amount) {
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length][amount + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int j = 1; j < amount + 1; j++) {
if (j >= coins[0]) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - coins[0]];
}
}
print(dp);
for (int i = 1; i < coins.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < amount + 1; j++) {
if (j >= coins[i]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - coins[i]];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
print(dp);
}
return dp[coins.length - 1][amount];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode518 leetcode = new ChangeMakingProblemLeetcode518();
// int count = leetcode.change(new int[]{1, 2, 5}, 5);
// int count = leetcode.change(new int[]{2}, 3);
// int count = leetcode.change(new int[]{15, 10, 1}, 21);
int count = leetcode.change(new int[]{25, 10, 5, 1}, 41);
System.out.println(count);
}
static void print(int[][] dp) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(18));
Object[] array = IntStream.range(0, dp[0].length + 1).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%2d ".repeat(dp[0].length)) + "%n", array);
for (int[] d : dp) {
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(("%2d ".repeat(d.length)) + "%n", array);
}
}
}注意,金额为 0 处需初始化为 1,且恒为 1,可以这么理解,当金额为 0 时,我们就只有一种组合凑满金额,那就是不用任何硬币
原因分析:
主要是因为状态转移的依赖
在动态规划过程中,我们依赖于已有的状态来更新新的状态。更新 dp[j] 时,状态转移是:
dp[j] += dp[j - coin];这表示:如果我们能够凑成金额 j - coin,那么就可以通过添加当前面额的硬币 coin 来凑成金额 j。
如果没有初始化 dp[0] = 1,那么当我们尝试用硬币 coin 来更新 dp[coin] 时,dp[coin - coin] 就会变成 dp[0],但如果 dp[0] 没有被初始化为 1,那就会导致计算出错。
降维
public int change(int[] coins, int amount) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int coin : coins) {
for (int j = coin; j < amount + 1; j++) {
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - coin];
}
}
return dp[amount];
}钢条切割
public class CutRodProblem {
/*
1 5 8 9
0 1 2 3 4
1 1 11 111 1111
(1) (2) (3) (4)
2 11 111 1111
2 21 211
22
(1) (5) (6) (10)
3 1 11 111 1111
2 21 211
3 22
31
(1) (5) (8) (10)
4 1 11 111 1111
2 21 211
3 22
31
4
(1) (5) (8) (10)
*/
static int cut(int[] values, int n) {
int[][] dp = new int[values.length][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
int v = values[i];
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
if (j >= i) {
dp[i][j] = Integer.max(dp[i - 1][j], v + dp[i][j - i]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
print(dp);
}
return dp[values.length - 1][n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(cut(new int[]{0, 1, 5, 8, 9}, 4));
}
}降维
static int cut(int[] values, int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
int v = values[i];
for (int j = i; j < n + 1; j++) {
dp[j] = Integer.max(dp[j], v + dp[j - i]);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return dp[n];
}本质上是完全背包问题,把钢条总长度看作背包容量,切分后的钢条看作物品。只是
此时的背包容量=物品数量,例如,钢条总长度为4,可以看作有四种物品:
长度1的钢条
长度2的钢条
长度3的钢条
长度4的钢条
另外,这个场景下,总能装满背包
最长公共子串
最长公共子串
给定两个字符串,输出其最长公共子串的长度
输入:AABCDJ FABCKK
输出:3
解释:最长公共子串为 ABC, 长度为 3。
公共子串:两个字符串中连续相等的部分
解决思路
- 定义状态:设定一个二维数组
dp,其中dp[i][j]表示以A[i - 1]为结尾与以B[j - 1]为结尾的最长公共子串的长度。 - 状态转移:
- 如果
A[i-1] == B[j-1],则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1。 - 否则,
dp[i][j] = 0。表示公共子串在当前位置没有得到延伸。
- 如果
- 初始化:
dp数组的第一行和第一列初始化为 0,表示空字符串与任何字符串的公共子串长度为 0。 - 结果:遍历
dp数组,找到其中的最大值,即为最长公共子串的长度。
public class LCSubstring {
static int lcs(String a, String b) {
int[][] dp = new int[b.length()][a.length()];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < b.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length(); j++) {
if (a.charAt(j) == b.charAt(i)) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
max = Integer.max(dp[i][j], max);
} else {
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
print(dp, a, b);
return max;
}
static void print(int[][] dp, String a, String b) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(23));
Object[] array = a.chars().mapToObj(i -> String.valueOf((char) i)).toArray();
System.out.printf(" "+"%2s ".repeat(a.length()) + "%n", array);
for (int i = 0; i < b.length(); i++) {
int[] d = dp[i];
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(b.charAt(i) + " " + "%2d ".repeat(d.length) + "%n", array);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(lcs("AABCDJ", "FABCKK"));
}
}最长重复子数组
public class Leetcode718 {
public int findLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length + 1;
int n = nums2.length + 1;
int[] dp = new int[n];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) {
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
max = Integer.max(max, dp[j]);
} else {
dp[j] = 0;
}
}
}
return max;
}
public int findLength1(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[j] = 1;
} else {
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
}
max = Integer.max(max, dp[j]);
} else {
dp[j] = 0;
}
}
}
return max;
}
public int findLength2(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int[][] dp = new int[nums1.length][nums2.length];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {
if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
max = Integer.max(max, dp[i][j]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode718 code = new Leetcode718();
System.out.println(code.findLength(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}, new int[]{3, 2, 1, 4, 7}));
System.out.println(code.findLength(new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, new int[]{1, 0, 0, 1, 1}));
}
}最长公共子序列
最长公共子序列
解决思路
- 定义状态: 设定一个二维数组
dp,其中dp[i][j]表示字符串A的前i个字符与字符串B的前j个字符的最长公共子序列的长度。 - 状态转移:
- 如果
A[i-1] == B[j-1],则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1。即,如果当前字符相同,最长公共子序列的长度加 1。 - 如果
A[i-1] != B[j-1],则dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])。即,如果当前字符不同,则最长公共子序列的长度取前一个字符的值(来自于A或B)。
- 如果
- 初始化:
dp数组的第一行和第一列初始化为 0,表示空字符串与任何字符串的公共子序列长度为 0。 - 结果:
dp[m][n](其中m是A的长度,n是B的长度)即为字符串A和B的最长公共子序列的长度。
public class LCSubsequence {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int m = text1.length();
int n = text2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
char a = text1.charAt(i - 1);
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
char b = text2.charAt(j - 1);
if (a == b) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Integer.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
print(dp, text2, text1);
return dp[m][n];
}
static void print(int[][] dp, String a, String b) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(23));
Object[] array = a.chars().mapToObj(i -> String.valueOf((char) i)).toArray();
System.out.printf(" " + "%2s ".repeat(a.length()) + "%n", array);
for (int i = 0; i < b.length(); i++) {
int[] d = dp[i + 1];
array = Arrays.stream(d).boxed().toArray();
System.out.printf(b.charAt(i) + " " + "%2d ".repeat(d.length) + "%n", array);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LCSubsequence code = new LCSubsequence();
System.out.println(code.longestCommonSubsequence("abcde", "ace"));
System.out.println(code.longestCommonSubsequence("ba", "yby"));
}
}两个字符串的删除操作
583. 两个字符串的删除操作 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public class Leetcode538 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode538 code = new Leetcode538();
System.out.println(code.minDistance("leetcode", "etco")); // 4
System.out.println(code.minDistance("eat", "sea")); // 2
System.out.println(code.minDistance("park", "spake")); // 3
}
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
char[] chars1 = word1.toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = word2.toCharArray();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
int x = chars1[i - 1];
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
int y = chars2[j - 1];
if (x == y) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Integer.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return m + n - dp[m][n] - dp[m][n];
}
}最长公共子串和最长公共子序列解决思路上的区别
这两个问题看起来很像,但是在解决思路上还是有较大差别的,以至于我最初尝试理解这两个问题的解决思路时很懵逼,饶了很多弯路,我在网上根本搜索不到有人分析这个问题,因此我决定把我的思路写下来。
状态转移条件: 在最长公共子序列中,即使当前字符不相等,dp[i][j] 也会取前一个状态的最大值,表示可以跳过当前字符;而在最长公共子串中,只有当前字符相等时,dp[i][j] 才会增加,否则为 0,表示公共子串结束。
结果存储位置: 在最长公共子序列中,最终结果存储在 dp[m][n] 中,其中 m 和 n 分别是字符串 A 和 B 的长度;而在最长公共子串中,结果是 dp 数组中的最大值。主要原因是因为状态转移条件的不一致,在最长公共子序列中,即使 A[i - 1] != B[j - 1],子问题状态也会被得到延续,而在最长公共子串中,如果A[i - 1] != B[j - 1],dp[i][j] 则会被置为0,以重新计算下一个公共子串的长度。
最长上升子序列
解决思路
- 定义状态:设定一个一维数组
dp,其中dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的最长上升子序列的长度 - 状态转移:对于每个元素
nums[i],遍历它前面每个元素nums[j],如果nums[i] > nums[j],则可以将nums[i]加入以nums[j]结尾的最长上升子序列中,也就是nums[i]可以作为原来以nums[j]结尾的最长上升子序列的新尾巴,此时更新dp[i]为dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)。 - 初始化:一开始可知每个元素自身可构成一个长度为 1 的上升子序列,因此初始化
dp[i] = 1。 - 结果:遍历
dp数组,找到其中的最大值, 即为整数数组nums的最长上升子序列的长度。
public class Leetcode300 {
/*
1 2 3 4
1 3 6 4 9
1 13 16 14 19
136 134 139
169
1369
149
1349
(1) (2) (3) (3) (4)
4
*/
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { // 满足了升序条件
// 用之前递增子序列的最大长度 + 1 更新当前长度
dp[i] = Integer.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return Arrays.stream(dp).max().getAsInt();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode300 code = new Leetcode300();
System.out.println(code.lengthOfLIS(new int[]{1, 3, 6, 4, 9}));
// System.out.println(code.lengthOfLIS(new int[]{10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18}));
// System.out.println(code.lengthOfLIS(new int[]{1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 4, 10, 5, 6}));
// 1 3 6 7 9 10 = 6
// 1 3 4 5 6 = 5
// System.out.println(code.lengthOfLIS(new int[]{0, 1, 0, 3, 2, 3}));
// System.out.println(code.lengthOfLIS(new int[]{7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7}));
}
}Catalan 数
出栈序列
n 个元素的入栈序列为:1,2,3,4,...,n,问有多少种可能的出栈序列
public class Catalan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(catalan(6));
}
static int catalan(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < n + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
System.out.print("(" + j + " " + (i - 1 - j) + ")\t");
dp[i] += dp[j] * dp[i - 1 - j];
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return dp[n];
}
}不同的二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int j = 2; j < n + 1; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
dp[j] += dp[i] * dp[j - 1 - i];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}括号生成
public class Leetcode22 {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
ArrayList<String>[] dp = new ArrayList[n + 1];
dp[0] = new ArrayList<>(List.of(""));
dp[1] = new ArrayList<>(List.of("()"));
for (int j = 2; j < n + 1; j++) {
dp[j] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) { // 第j个卡特兰数的拆分
System.out.printf("(%d,%d)\t", i, j - 1 - i);
// dp[j] += dp[i] * dp[j - 1 - i];
// dp[j].add("(" + dp[i] + ")" + dp[j - 1 - i]);
for (String k1 : dp[i]) {
for (String k2 : dp[j - 1 - i]) {
dp[j].add("(" + k1 + ")" + k2);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[j]);
}
return dp[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Leetcode22 code = new Leetcode22();
System.out.println(code.generateParenthesis(4));
}
}打家劫舍
public class HouseRobberLeetcode198 {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int[] dp = new int[len];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Integer.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) {
dp[i] = Integer.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]);
}
return dp[len - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HouseRobberLeetcode198 code = new HouseRobberLeetcode198();
System.out.println(code.rob(new int[]{2, 7, 9, 3, 1}));
System.out.println(code.rob(new int[]{2, 1, 1, 2}));
}
}降维
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int a = nums[0];
int b = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
int c = Math.max(b, nums[i] + a);
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}Travelling salesman problem
旅行商问题
一个售货员必须访问n个城市,恰好访问每个城市一次,并最终回到出发城市。售货员从城市 i 到城市 j 的旅行费用是一个整数,旅行所需的全部费用是他旅行经过的的各边费用之和,而售货员希望使整个旅行费用最低。
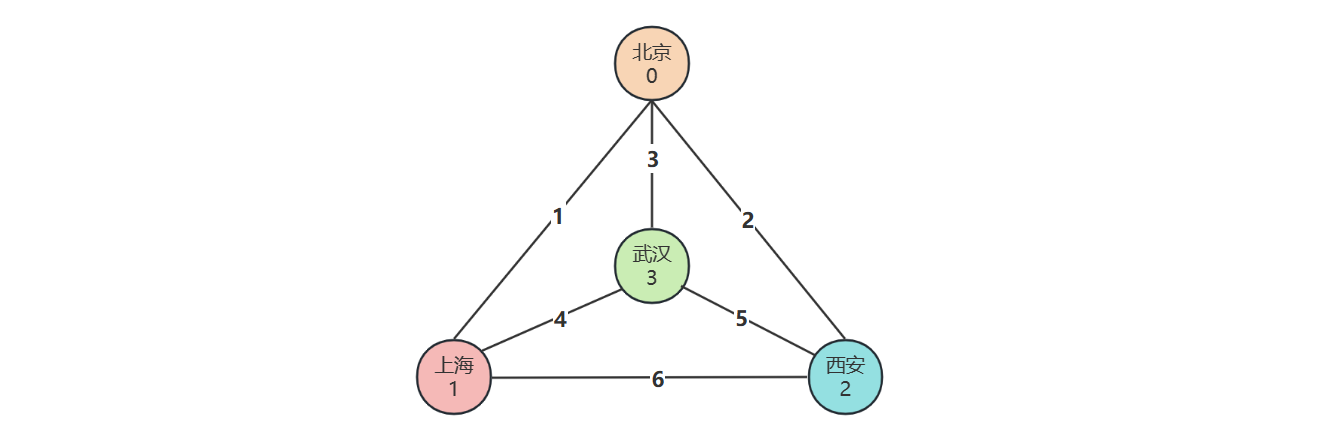
public class TravellingSalesmanProblem {
/*
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 1 0 6 4
2 2 6 0 5
3 3 4 5 0
出发城市 i
剩余城市集合 j
遍历 j 时的变量 k (剩余的某一个城市)
d(i, j) => min(
g[i][k] + d(k, j去掉k)
g[i][k] + d(k, j去掉k)
g[i][k] + d(k, j去掉k)
)
d(k,空) => 从k回到起点 => g[k][i]
d(出发城市, 剩余城市集合) ==> 从出发城市开始,走完剩余城市,花费的最少代价
d(0,1|2) => g[0][1] + d(1,2)
=> g[0][2] + d(2,1)
d(1,1|2)
d(2,1|2)
d(3,1|2) => g[3][1] + d(1,2)
=> g[3][2] + d(2,1)
d(0,{1,2,3}) => c01+d(1,{2,3}) => c12+d(2,{3}) => c23+d(3,{})
c13+d(3,{2}) => c32+d(2,{})
c02+d(2,{1,3}) => c21+d(1,{3}) => c13+d(3,{})
c23+d(3,{1}) => c31+d(1,{})
c03+d(3,{1,2}) => c31+d(1,{2}) => c12+d(2,{})
c32+d(2,{1}) => c21+d(1,{})
d(0,{1}) => c01+d(1,{}) 0->1->0
d(1,{1})
d(2,{1}) => c21+d(1,{}) 2->1->0
d(3,{1}) => c31+d(1,{}) 3->1->0
d(0,{2}) => c02+d(2,{}) 0->2->0
d(1,{2}) => c12+d(2,{}) 1->2->0
d(2,{2})
d(3,{2}) => c32+d(2,{}) 3->2->0
d(0,{1,2}) => c01+d(1,{2}) => 0->1->2->0
c02+d(2,{1}) => 0->2->1->0
d(3,{1,2}) => c31+d(1,{2}) => 3->1->2->0
c32+d(2,{1}) => 3->2->1->0
d(0,{3}) => c03+d(3,{}) 0->3->0
d(1,{3}) => c13+d(3,{}) 1->3->0
d(2,{3}) => c23+d(3,{}) 2->3->0
d(3,{3})
d(0,{1,3}) => c01+d(1,{3}) => 0->1->3->0
c03+d(3,{1}) => 0->3->1->0
d(2,{1,3}) => c21+d(1,{3}) => 2->1->3->0
c23+d(3,{1}) => 2->3->1->0
d(0,{2,3}) => c02+d(2,{3}) => 0->2->3->0
c03+d(3,{2}) => 0->3->2->0
d(1,{2,3}) => c12+d(2,{3}) => 1->2->3->0
c13+d(3,{2}) => 1->3->2->0
d(0,{1,2,3}) => c01+d(1,{2,3}) 11+1
c02+d(2,{1,3}) 10+2
c03+d(3,{1,2}) 12+3
0 1 2 12 3 13 23 123
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 0 2 4 9 6 8 10 12
1 1 _ 8 _ 7 _ 11 _
2 2 7 _ _ 8 10 _ _
3 3 5 7 12 _ _ _ _
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 2, 3},
{1, 0, 6, 4},
{2, 6, 0, 5},
{3, 4, 5, 0},
};
// System.out.println(tsp(graph));
System.out.println(6 >> (0-1));
}
static int tsp1(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
int[][] dp = new int[1 << n][n];
for (int[] row : dp) {
Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2);
}
dp[1][0] = 0;
for (int mask = 1; mask < 1 << n; mask++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ((mask & 1 << i) == 0) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if ((mask & 1 << j) != 0) continue;
dp[mask | 1 << j][j] = Math.min(dp[mask | 1 << j][j], dp[mask][i] + graph[i][j]);
}
}
print(dp);
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = Math.min(res, dp[(1 << n) - 1][i] + graph[i][0]);
}
return res;
}
/*
110 是否包含 0 = 0 & 1 = 0
110 是否包含 1 = 110 & 1 = 0
110 是否包含 2 = 11 & 1 = 1
110 是否包含 3 = 1 & 1 = 1
110 是否包含 4 = 0 & 1 = 0
*/
static boolean contains(int set, int city) {
return (set >> (city - 1) & 1) == 1;
}
/*
110 110
^100 ^010
---- ----
10 100
*/
static int exclude(int set, int city) {
return set ^ (1 << (city - 1));
}
static int tsp(int[][] g) {
int n = g.length;
int m = 1 << (n - 1);
int[][] dp = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][0] = g[i][0];
}
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2;
if (contains(j, i)) continue;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k++) {
if (contains(j, k)) {
// System.out.println("(" + k + "," + (j ^ (1 << (k - 1))) + ")");
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], g[i][k] + dp[k][exclude(j, k)]);
}
}
}
print(dp);
}
return dp[0][m - 1];
}
static void print(int[][] dist) {
System.out.println("-------------------------");
for (int[] row : dist) {
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(row).boxed()
.map(x -> x >= Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ? "∞" : String.valueOf(x))
.map(s -> String.format("%2s", s))
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", "]")));
}
}
}分治(Divide and Conquer)
核心思想
- 将大问题划分为两个到多个子问题
- 子问题可以继续拆分成更小的子问题,直到能够简单求解
- 如有必要,将子问题的解进行合并,得到原始问题的解
分治的应用
- 二分查找
- 快速排序
- 归并排序
- 合并K个排序链表
二分查找
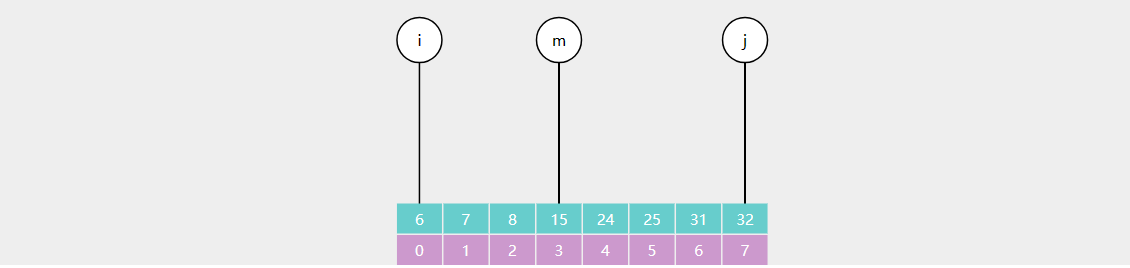
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int target) {
return recursion(a, target, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static int recursion(int[] a, int target, int i, int j) {
if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (target < a[m]) {
return recursion(a, target, i, m - 1);
} else if (a[m] < target) {
return recursion(a, target, m + 1, j);
} else {
return m;
}
}减而治之,每次搜索范围内元素减少一半
快速排序
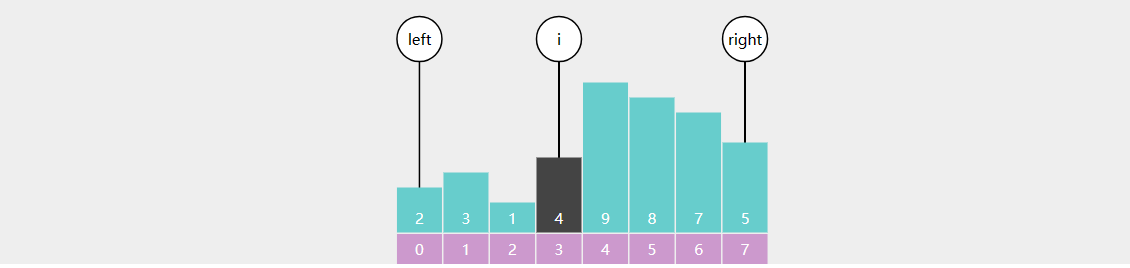
public static void sort(int[] a) {
quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
int p = partition(a, left, right);
quick(a, left, p - 1);
quick(a, p + 1, right);
}分而治之,这次分区基准点,在划分后两个区域分别进行下次分区
归并排序
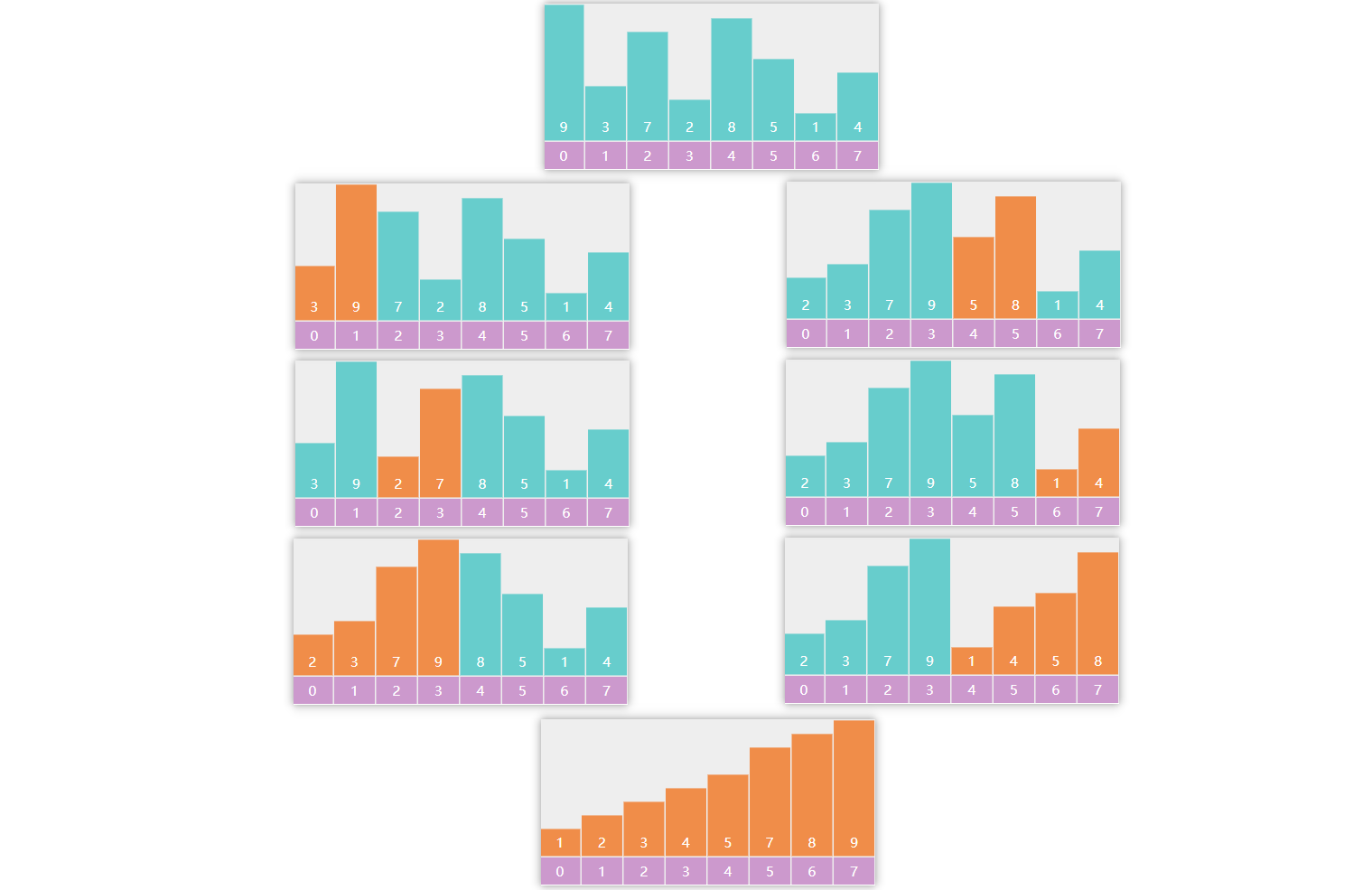
public static void sort(int[] a1) {
int[] a2 = new int[a1.length];
split(a1, 0, a1.length - 1, a2);
}
private static void split(int[] a1, int left, int right, int[] a2) {
int[] array = Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, left, right + 1);
// 2. 治
if (left == right) {
return;
}
// 1. 分
int m = (left + right) >>> 1;
split(a1, left, m, a2);
split(a1, m + 1, right, a2);
// 3. 合
merge(a1, left, m, m + 1, right, a2);
System.arraycopy(a2, left, a1, left, right - left + 1);
}分而治之,分到区间内只有一个元素,合并区间
**合并K个排序链表 **
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return split(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode split(ListNode[] lists, int i, int j) {
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
if (j == i) {
return lists[i];
}
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(
split(lists, i, m),
split(lists, m + 1, j)
);
}分而治之,分到区间内只有一个链表,合并区间
对比动态规划
- 都需要拆分子问题
- 动态规划的子问题有重叠、因此需要记录之前子问题解,避免重复运算
- 分而治之的子问题无重叠
快速选择算法
public class Utils {
static int quick(int[] a, int left, int right, int index) {
int p = partition(a, left, right);
if (p == index) {
return a[p];
}
if (p < index) {
return quick(a, p + 1, right, index);
} else {
return quick(a, left, p - 1, index);
}
}
static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(right - left + 1) + left;
swap(a, left, idx);
int pv = a[left];
int i = left + 1;
int j = right;
while (i <= j) {
// i 从左向右找大的或者相等的
while (i <= j && a[i] < pv) {
i++;
}
// j 从右向左找小的或者相等的
while (i <= j && a[j] > pv) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
swap(a, i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
}
swap(a, j, left);
return j;
}
static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
}数组中第k个最大元素
public class FindKthLargestLeetcode215 {
/*
目标 index = 4
3 2 1 5 6 4
=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (3)
=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (5)
=> 3 2 1 4 5 6 (4)
*/
public int findKthLargest(int[] a, int k) {
return Utils.quick(a, 0, a.length - 1, a.length - k);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 应为5
FindKthLargestLeetcode215 code = new FindKthLargestLeetcode215();
System.out.println(code.findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 2));
// 应为4
System.out.println(code.findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5, 5, 6}, 4));
}
}数组中位数
public class FindMedian {
/*
偶数个
3 1 5 4
奇数个
4 5 1
4 5 1 6 3
*/
public static double findMedian(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length % 2 != 0) {
return findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2);
} else {
System.out.println((nums.length / 2 - 1) + "," + (nums.length / 2));
int a = findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2);
int b = findIndex(nums, nums.length / 2 - 1);
return (a + b) / 2.0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{3, 1, 5, 4}));
System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{3, 1, 5, 4, 7, 8}));
System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{4, 5, 1}));
System.out.println(findMedian(new int[]{4, 5, 1, 6, 3}));
}
static int findIndex(int[] a, int index) {
return Utils.quick(a, 0, a.length - 1, index);
}
}平方根整数部分
public class SqrtLeetcode69 {
static int mySqrt(int x) {
int i = 1;
int j = x;
while (i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (m <= x / m) {
i = m + 1;
} else {
j = m - 1;
}
}
return j;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(mySqrt(1));
System.out.println(mySqrt(2));
System.out.println(mySqrt(4));
System.out.println(mySqrt(8));
System.out.println(mySqrt(9));
}
}- while(i <= j) 含义是在此区间内,只要有数字还未尝试,就不算结束
- j 最后指向的数刚好是最后一个平方小于等于 x 的数,也就是题目要求的平方根整数部分
- 使用除法而非乘法,避免大数相乘越界
- i 从1开始是为了避免出现 m = 0 的情况
至少k个重复字符的最长子串
395. 至少有 K 个重复字符的最长子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public class LongestSubstringLeetcode395 {
// s.length() < k "a" 2
static int longestSubstring1(String s, int k) {
// 子串落选情况
if (s.length() < k) {
return 0;
}
int[] counts = new int[26]; // 索引对应字符 值用来存储该字符出现了几次
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) { // 'a' -> 0 'b' -> 1 ....
counts[c - 'a']++;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(counts));
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char c = chars[i];
int count = counts[c - 'a']; // i字符出现次数
if (count < k) {
int j = i + 1;
while(j < s.length() && counts[chars[j] - 'a'] < k) {
j++;
}
System.out.println(s.substring(0, i) + "\t" + s.substring(j));
return Integer.max(
longestSubstring1(s.substring(0, i), k),
longestSubstring1(s.substring(j), k)
);
}
}
// 子串入选情况
return s.length();
}
public static int longestSubstring(String s, int k) {
return f(s.toCharArray(), k, 0, s.length() - 1);
}
static int f(char[] chars, int k, int l, int r) {
if (r - l + 1 < k) {
return 0;
}
int[] counts = new int[26];
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
counts[chars[i] - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
int count = counts[chars[i] - 'a'];
if (count < k) {
int j = i + 1;
while (j < r && counts[chars[j] - 'a'] < k) {
j++;
}
return Math.max(f(chars, k, l, i - 1), f(chars, k, j, r));
}
}
return r - l + 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// i j
System.out.println(longestSubstring("aaaccbbb", 3)); // ababb
// System.out.println(longestSubstring1("dddxaabaaabaacciiiiefbff", 3));
// System.out.println(longestSubstring("ababbc", 3)); // ababb
// System.out.println(longestSubstring("ababbc", 2)); // ababb
/*
ddd aabaaabaa iiii fbff
aa aaa aa f ff
统计字符串中每个字符的出现次数,移除哪些出现次数 < k 的字符
剩余的子串,递归做此处理,直至
- 整个子串长度 < k (排除)
- 子串中没有出现次数 < k 的字符
*/
}
}回溯(Backtracking Algorithm)
核心思想
- 程序在运行过程中分成了多个阶段
- 通过某些手段,将数据恢复到之前某一阶段,这就称之为回溯
- 手段包括:方法栈、自定义栈
全排列
public class PermuteLeetcode46 {
static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> r = new ArrayList<>();
rec(nums, visited, stack, r);
return r;
}
static void rec(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> r) {
if (stack.size() == nums.length) {
r.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(visited[i]){
continue;
}
stack.push(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
rec(nums, visited, stack, r);
//归的时候要记得把变量状态回退到上一个方法原来的状态,也就是回溯
stack.pop();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> permute = permute(new int[]{1, 2, 3});
for (List<Integer> s : permute) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}全排列II
public class PermuteLeetcode47 {
static List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nums, new boolean[nums.length], new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (stack.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !visited[i-1]) { // 找出重复数字
continue;
}
if (!visited[i]) {
stack.push(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
dfs(nums, visited, stack, result);
visited[i] = false;
stack.pop();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 3};
List<List<Integer>> permute = permuteUnique(nums);
for (List<Integer> list : permute) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}- 排好序,这样重复的数字会相邻,主要是为了让重复数字只会连续存在,更好判断前一个重复数字存在的位置
- 定好规则:必须 1 固定之后才能固定 1',即 1 的 visited = true 才能继续处理 1'
- 在遍历时,遇到了
nums[i] == nums[i - 1](即 1 和 1‘ 这种情况),进一步检查 i-1 位置的数字有没有 visited,没有,则不处理(剪枝) - 其实就是在相同数字的内部给它们指定一个既定的顺序,比如说,第一个 1 必须第一个被访问, 第二个 1 必须第二个被访问,然后以此类推
组合
public class CombinationLeetcode77 {
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(n, k, 1, new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static int count = 0;
static void dfs(int n, int k, int start, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
count++;
if (k == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
System.out.println(stack);
return;
}
// if (k > n - start + 1) { return; }
for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) {
// System.out.printf("k-1=%d n=%d i=%d %n", k - 1, n, i);
if (k > n - i + 1) {
continue;
}
stack.push(i);
dfs(n, k - 1, i + 1, stack, result);
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum(5, 4);
// for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
// System.out.println(list);
// }
System.out.println(count);
}
}剪枝
- k 代表剩余要组合的个数
n - i + 1代表剩余可用数字- 剪枝条件是:剩余可用数字小于剩余要组合的个数
- 为啥放在循环外面不行?即这行代码:
if (k > n - start + 1) { return; }- 因为它只考虑了 start 一种情况,而实际在循环内要处理的是 start,start+1 ... n 这多种情况
似乎 ArrayList 作为 stack 性能高一些,见下面代码,但是这道题在 leetcode 上执行时间不稳定,相同代码都会有较大时间差异(15ms vs 9ms)
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(k == 0 || n < k) return result;
dfs(n, k, 1, new ArrayList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int n, int k, int start, ArrayList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (k == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) {
if (k-1 > n - i) {
continue;
}
stack.add(i);
dfs(n, k - 1, i + 1, stack, result);
stack.remove(stack.size()-1);
}
}
}组合总和
public class CombinationLeetcode39 {
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(target, 0,candidates, new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int target, int start, int[] candidates, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int candidate = candidates[i];
if (target < candidate) {
continue;
}
stack.push(candidate);
dfs(target - candidate, i, candidates, stack, result);
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum(new int[]{6, 3, 2, 7}, 7);
for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}与之前的零钱兑换问题其实是一样的,只是
- 本题求的是:所有组合的具体信息
- 零钱兑换问题求的是:所有组合中数字最少的、所有组合个数...
组合总和 II
public class CombinationLeetcode40 {
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(target, 0, candidates, new boolean[candidates.length], new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int target, int start, int[] candidates, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int candidate = candidates[i];
if (target < candidate) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && candidate == candidates[i - 1] && !visited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
stack.push(candidate);
dfs(target - candidate, i + 1, candidates, visited, stack, result);
stack.pop();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] candidates = {10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum2(candidates, 8);
for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}组合总和 III
public class CombinationLeetcode216 {
// 此 target 代表数字组合后的和
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(1, target, k, new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static int count = 0;
static void dfs(int start, int target, int k,
LinkedList<Integer> stack,
List<List<Integer>> result) {
// System.out.println(stack);
count++;
if (target == 0 && stack.size() == k) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {
// 还差几个数字 剩余可用数字
/*if (k - stack.size() > 9 - i + 1) {
continue;
}*/
if(target < i){
continue;
}
if(stack.size() == k) {
continue;
}
stack.push(i);
dfs(i + 1, target - i, k, stack, result);
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum3(3, 7);
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum3(2, 18); // 9 8
for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
System.out.println(list);
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}这道题更类似于 77 题,区别在于
- 77 题的数字范围 n 更大 [1,20],而本题数字范围限制为 [1,9]
- 本题不仅仅找到组合,还要让组合之和等于 target(类似于 39 题)
剪枝优化
- 如果剩余的和 target 还没 i 大,这时减完 i 是负数,肯定无法满足要求,因此有剪枝条件:
target < i
- 如果组合的数字个数已经到达了上限 k,还没有凑够 target,也没必要继续递归,因此有:
stack.size() == k
N 皇后
public class NQueenLeetcode51 {
static List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] table = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(table[i], '.');
}
dfs(0, n, table, result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int i, int n, char[][] table, List<List<String>> result) {
if (i == n) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : table) {
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
result.add(list);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (notValid(table, i, j)) {
continue;
}
table[i][j] = 'Q';
dfs(i + 1, n, table, result);
table[i][j] = '.';
}
}
/*
. . . .
. . . .
. ? . .
. . . .
*/
static boolean notValid(char[][] table, int row, int col) {
int n = table.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (table[i][col] == 'Q') { // 上
return true;
}
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (table[i][j] == 'Q') {
return true;
}
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (table[i][j] == 'Q') {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for (List<String> table : solveNQueens(8)) {
for (String row : table) {
System.out.println(row);
}
count++;
System.out.println("--------------------- " + count);
}
}
}public class NQueenLeetcode51 {
static List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] table = new char[n][n];
boolean[] va = new boolean[n];
boolean[] vb = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
boolean[] vc = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(table[i], '.');
}
dfs(0, n, table, result, va, vb, vc);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int i, int n, char[][] table, List<List<String>> result, boolean[] va, boolean[] vb, boolean[] vc) {
if (i == n) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : table) {
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
result.add(list);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (va[j] || vb[i + j] || vc[i - j + n - 1]) {
continue;
}
va[j] = true;
vb[i + j] = true;
vc[i - j + n - 1] = true;
table[i][j] = 'Q';
dfs(i + 1, n, table, result, va, vb, vc);
table[i][j] = '.';
va[j] = false;
vb[i + j] = false;
vc[i - j + n - 1] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for (List<String> table : solveNQueens(4)) {
for (String row : table) {
System.out.println(row);
}
count++;
System.out.println("--------------------- " + count);
}
}
}解数独
public class SudokuLeetcode37 {
record Pair(int i, int j) {
}
static void solveSudoku(char[][] table) {
int n = 9;
boolean[][] va = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][] vb = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][][] vc = new boolean[3][3][n];
List<Pair> blanks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (table[i][j] != '.') {
int x = table[i][j] - '0' - 1;
va[i][x] = true;
vb[j][x] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
} else {
blanks.add(new Pair(i, j));
}
}
}
dfs(0, blanks, table, va, vb, vc);
}
static boolean dfs(int p, List<Pair> blanks, char[][] table, boolean[][] va, boolean[][] vb, boolean[][][] vc) {
if (p == blanks.size()) {
print(table);
return true;
}
int n = table.length;
for (int d = 0; d < n; d++) {
Pair pair = blanks.get(p);
if (va[pair.i][d] || vb[pair.j][d] || vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d]) {
continue;
}
char ch = (char) (d + '0' + 1);
table[pair.i][pair.j] = ch;
va[pair.i][d] = true;
vb[pair.j][d] = true;
vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d] = true;
boolean dfs = dfs(p + 1, blanks, table, va, vb, vc);
if (dfs) {
return true;
}
table[pair.i][pair.j] = '.';
va[pair.i][d] = false;
vb[pair.j][d] = false;
vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d] = false;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table = {
{'5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'},
{'6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'},
{'.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'},
{'8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'},
{'4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'},
{'7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'},
{'.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'},
{'.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9'}
};
solveSudoku(table);
print(table);
}
static char[][] solved = {
{'5', '3', '4', '6', '7', '8', '9', '1', '2'},
{'6', '7', '2', '1', '9', '5', '3', '4', '8'},
{'1', '9', '8', '3', '4', '2', '5', '6', '7'},
{'8', '5', '9', '7', '6', '1', '4', '2', '3'},
{'4', '2', '6', '8', '5', '3', '7', '9', '1'},
{'7', '1', '3', '9', '2', '4', '8', '5', '6'},
{'9', '6', '1', '5', '3', '7', '2', '8', '4'},
{'2', '8', '7', '4', '1', '9', '6', '3', '5'},
{'3', '4', '5', '2', '8', '6', '1', '7', '9'}
};
static void print(char[][] table) {
for (char[] chars : table) {
System.out.println(new String(chars));
}
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(table, solved));
}
}public class SudokuLeetcode37 {
static void solveSudoku(char[][] table) {
int n = 9;
boolean[][] va = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][] vb = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][][] vc = new boolean[3][3][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (table[i][j] != '.') {
int x = table[i][j] - '0' - 1;
va[i][x] = true;
vb[j][x] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(table, va, vb, vc, 0, 0);
}
static boolean dfs(char[][] table, boolean[][] va, boolean[][] vb, boolean[][][] vc, int i, int j) {
while (table[i][j] != '.') {
if (++j >= 9) {
j = 0;
i++;
}
if (i >= 9) {
return true;
}
}
int n = table.length;
for (int d = 0; d < n; d++) {
if (va[i][d] || vb[j][d] || vc[i / 3][j / 3][d]) {
continue;
}
char ch = (char) (d + '0' + 1);
table[i][j] = ch;
va[i][d] = true;
vb[j][d] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][d] = true;
boolean dfs = dfs(table, va, vb, vc, i, j);
if (dfs) {
return true;
}
table[i][j] = '.';
va[i][d] = false;
vb[j][d] = false;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][d] = false;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table = {
{'5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'},
{'6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'},
{'.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'},
{'8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'},
{'4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'},
{'7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'},
{'.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'},
{'.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9'}
};
solveSudoku(table);
print(table);
}
static char[][] solved = {
{'5', '3', '4', '6', '7', '8', '9', '1', '2'},
{'6', '7', '2', '1', '9', '5', '3', '4', '8'},
{'1', '9', '8', '3', '4', '2', '5', '6', '7'},
{'8', '5', '9', '7', '6', '1', '4', '2', '3'},
{'4', '2', '6', '8', '5', '3', '7', '9', '1'},
{'7', '1', '3', '9', '2', '4', '8', '5', '6'},
{'9', '6', '1', '5', '3', '7', '2', '8', '4'},
{'2', '8', '7', '4', '1', '9', '6', '3', '5'},
{'3', '4', '5', '2', '8', '6', '1', '7', '9'}
};
static void print(char[][] table) {
for (char[] chars : table) {
System.out.println(new String(chars));
}
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(table, solved));
}
}